
Types of Forests (in India)
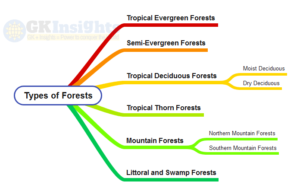
- Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Semi-Evergreen Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Moist Deciduous
- Dry Deciduous
- Tropical Thorn Forests
- Mountain Forests
- Northern Mountain Forests
- Southern Mountain Forests
- Littoral and Swamp Forests
Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Locations: Western Ghats, north-eastern hills, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Climate: Warm, humid, over 200 cm annual rainfall.
- Features: Trees up to 60m, green all year.
- Species: Rosewood, mahogany, aini, ebony.
Semi-Evergreen Forests
- Locations: Less rainy parts of evergreen regions.
- Features: Mix of evergreen and moist deciduous trees.
- Species: White cedar, hollock, kail.
Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Locations: Most widespread in India.
- Climate: Rainfall between 70-200 cm.
- Types: Moist and dry deciduous.
Moist Deciduous
- Locations: North-eastern states, foothills of Himalayas, Western Ghats, Odisha.
- Species: Teak, sal, shisham, hurra, mahua, amla, semul, kusum, sandalwood.
Dry Deciduous
- Locations: Peninsula, plains of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- Features: Transition zones based on rainfall.
Tropical Thorn Forests
- Locations: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh.
- Climate: Less than 50 cm rainfall.
- Features: Grasses and shrubs.
Mountain Forests
- Locations: Himalayan ranges.
- Features: Vegetation changes with altitude.
- Types: Northern and southern mountain forests.
Northern Mountain Forests
- Locations: Himalayan ranges.
- Features: Altitude-based vegetation.
- Species: Oak, chestnut, pine, Deodar, chinar, walnut, blue pine, spruce.
Southern Mountain Forests
- Locations: Higher hill ranges of north-eastern India, West Bengal, Uttarakhand.
- Species: Chir Pine, Deodar.
Littoral and Swamp Forests
- Locations: Coastal regions, deltas.
- Features: Mangroves, salt-tolerant vegetation.
- Importance: Biodiversity hotspots, need for conservation.
Mangrove Forests
- Coverage: 6,740 sq. km in India.
- Locations: Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Sunderbans, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna deltas.
- Conservation Needs: High.
Forest Cover Statistics
- State Records: 23.28% of total land area.
- Actual Cover: Varies by state.
- Low Forest Area States: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi.
Forest & Natural Vegetation Conservation
Government Policies
- Policy: Adopted in 1952, modified in 1988.
Social Forestry
Categories: Farm, Urban & Rural forestry.
- Farm Forestry: Farmers grow Trees (instead of Crops)
- Urban Forestry: Green belts, parks, roadside avenues
- Rural Forestry: Agro-forestry and community-forestry.
Wildlife Conservation
- Act: Wildlife Act of 1972
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MOEFCC) is implementing several schemes for environmental conservation
- National Parks: 106 NPs in India
- Wildlife sanctuaries: 567 WLSs in India.
- Project Tiger: 54 Tiger Reserves in India.
- Project Elephant: 33 Elephant Reserves in India.
- Ramsar Sites: 75 in India
- Biosphere Reserves: 18 in India.
Best of Luck for UPSC preparation! – gkinsights.com
Also Check: 22 Nuclear Power Plants in India – Map & List
