
Election Commision of India (ECI)’s Structure, Roles, Mindmap for UPSC
Introduction
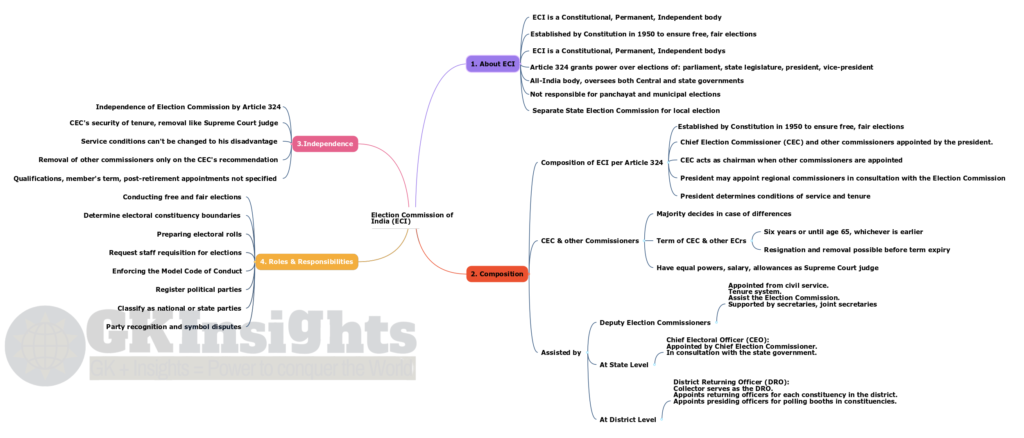
- Established by Constitution in 1950 to ensure free, fair elections
- ECI is a Constitutional, Permanent, Independent body
- Article 324 grants power over elections of: parliament, state legislature, president, vice-president
- All-India body, oversees both Central and state governments
- Not responsible for panchayat and municipal elections
- Separate State Election Commission for local elections
ECI Mindmap
Mindmap on ‘Election Commission of India (ECI)’ with information relevant to UPSC.
(Note: Open image in new tab for proper view.)
Composition
- Composition of Election Commission per Article 324:
- Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and other commissioners appointed by the president.
- CEC acts as chairman when other commissioners are appointed.
- President may appoint regional commissioners in consultation with the Election Commission.
- President determines conditions of service and tenure.
- CEC & other Commissioners have equal powers, salary, allowances as Supreme Court judge.
- Majority decides in case of differences.
- Term (of CEC & other ECrs):
- Six years or until age 65, whichever is earlier.
- Resignation and removal possible before term expiry.
- Election Commission assisted by:
- Deputy Election Commissioners:
- Appointed from civil service.
- Tenure system.
- Assist the Election Commission.
- Supported by secretaries, joint secretaries, deputy secretaries, and under secretaries in the commission’s secretariat.
- State Level:
- Chief Electoral Officer (CEO):
- Appointed by Chief Election Commissioner.
- In consultation with the state government.
- District Level:
- District Returning Officer (DRO)
- Collector serves as the DRO.
- Appoints returning officers for each constituency in the district.
- Appoints presiding officers for polling booths in constituencies.
- Deputy Election Commissioners:
Also Check: Preamble of the Constitution
Independence and Autonomy
- Independence of Election Commission by Article 324
- Chief Election Commissioner’s security of tenure, removal like Supreme Court judge – by the president, only on a resolution passed by both Houses of Parliament with special majority, based on proved misbehavior or incapacity.
- Service conditions can’t be changed to his disadvantage.
- Removal of other commissioners only on the chief election commissioner’s recommendation.
- Flaws: Qualifications, term of members, and post-retirement appointments not specified
Roles and Responsibilities
- Conducting free and fair elections.
- Determine electoral constituency boundaries, Preparing electoral rolls.
- Request staff requisition for elections, Enforcing the Model Code of Conduct.
- Register political parties and classify as national or state parties.
- Act as a court for party recognition and symbol disputes.
- Managing election schedules, Counting and declaring results.
- Cancel polls in cases of irregularities, rigging, or violence.
